[2025] Unlocking Quantum Potential: Google's Quest with UK Experts
Quantum computing has long been heralded as the next big leap in computational power, promising to solve problems that are currently beyond the reach of classical computers. Google's recent initiative to partner with UK experts to explore potential applications of their quantum chip, Willow, marks a significant step in making quantum computing accessible and practical for a wider range of fields.
In this article, we will explore the intricacies of quantum computing, the specific capabilities of Google's Willow processor, and the practical applications and challenges associated with this cutting-edge technology. We'll delve into the potential uses in various sectors, provide a practical implementation guide, and discuss future trends and recommendations for harnessing quantum technology effectively.
TL; DR
- Key Point 1: Google's collaboration with UK experts aims to explore quantum computing's applications, particularly using the Willow processor.
- Key Point 2: Quantum computing can revolutionize fields like chemistry, medicine, and cryptography by solving complex problems beyond classical limits.
- Key Point 3: Practical implementation challenges include error rates, scalability, and the need for specialized algorithms.
- Key Point 4: Future trends point towards hybrid systems combining classical and quantum computing for optimal performance.
- Bottom Line: Quantum computing holds immense potential, but requires careful implementation and development to unlock its full capabilities.

Understanding Quantum Computing
Quantum computing operates on principles fundamentally different from classical computing. At its core, quantum computing utilizes quantum bits, or qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously, thanks to the principles of superposition and entanglement. This capability allows quantum computers to process a vast amount of information at once, potentially solving complex problems much faster than classical computers.
The quantum computing architecture is designed to perform specific types of calculations more efficiently than classical computers. Quantum algorithms, such as Shor's algorithm for factoring large numbers and Grover's algorithm for searching unsorted databases, demonstrate the potential speed advantages of quantum computing.
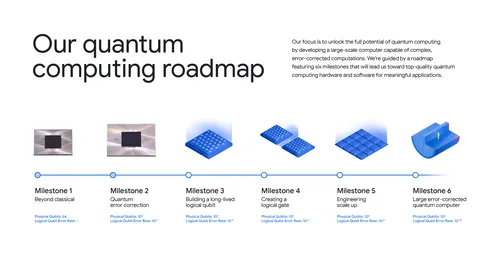
The Willow Processor: A Technological Marvel
Google's Willow processor is one of the leading advancements in quantum hardware. Built using superconducting qubits, Willow is designed to maximize coherence time and minimize error rates, two critical factors in quantum computing performance.
Key Features of Willow
- Superconducting Qubits: These qubits are cooled to near absolute zero, reducing noise and increasing stability.
- Error Correction: Advanced error correction techniques help mitigate the effects of decoherence and operational errors.
- Scalability: Willow is designed with scalability in mind, allowing for future expansion as technology develops.
Google's partnership with UK researchers aims to leverage these features to explore practical applications across various domains.
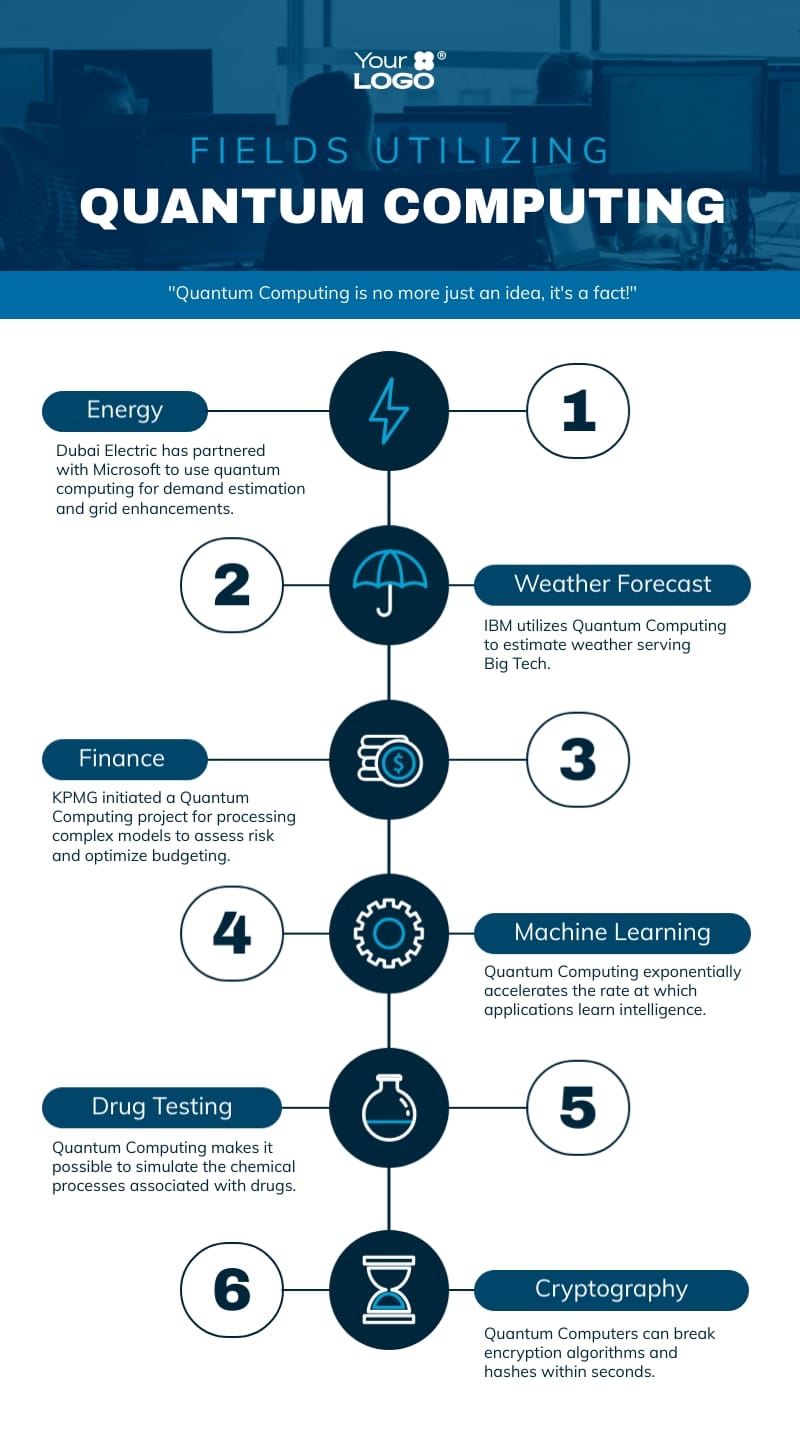
Practical Applications of Quantum Computing
Chemistry and Material Science
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize chemistry and material science by accurately simulating molecular interactions and chemical reactions at an atomic level. This capability can lead to the discovery of new materials and the development of more efficient catalysts.
Example Use Case
Consider the challenge of developing a new drug. Quantum computers can simulate the interaction between a drug molecule and its target protein with unprecedented accuracy, potentially reducing the time and cost of drug discovery significantly.
Medicine and Healthcare
In healthcare, quantum computing can enhance the analysis of complex biological data, leading to more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans. Machine learning algorithms, when run on quantum systems, can process vast datasets and uncover patterns that are invisible to classical algorithms.
Case Study: Cancer Treatment
Researchers are investigating the use of quantum computing to analyze genomic data for personalized cancer treatment. By identifying specific genetic mutations, quantum algorithms can suggest tailored therapies for individual patients.
Cryptography and Security
Quantum computing poses both opportunities and challenges for cryptography. While it can break many of the cryptographic systems currently in use, it also offers the potential for developing new, more secure encryption methods based on quantum principles.
Optimization Problems
Many industries face complex optimization problems, from logistical planning to financial modeling. Quantum computing's ability to evaluate numerous possibilities simultaneously makes it ideal for finding optimal solutions to these problems.
Example: Supply Chain Management
Quantum algorithms can optimize supply chain logistics by evaluating countless routing scenarios, improving efficiency, and reducing costs.
Implementation Guide: Harnessing Quantum Power
Step-by-Step Implementation
- Identify Suitable Problems: Not all problems benefit from quantum computing. Focus on those with high complexity and large datasets.
- Develop Quantum Algorithms: Tailor existing quantum algorithms to your specific needs or develop new ones if necessary.
- Leverage Hybrid Systems: Combine quantum and classical systems to maximize computational efficiency.
- Invest in Error Correction: Implement robust error correction methods to enhance reliability.
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
- High Error Rates: Implement advanced error correction and noise mitigation strategies.
- Scalability Issues: Design systems with modular scalability in mind to accommodate future growth.
- Algorithm Limitations: Continuously update and optimize algorithms to improve performance.
Future Trends in Quantum Computing
Hybrid Quantum-Classical Systems
The future of quantum computing likely involves hybrid systems that leverage the strengths of both quantum and classical computing. Such systems can handle a broader range of tasks, optimizing performance and efficiency.
Advances in Quantum Hardware
Ongoing research aims to develop more stable and scalable qubits, improving coherence times and reducing error rates. Innovations in materials and quantum chip design will play a pivotal role in this evolution.
Quantum Computing in the Cloud
Cloud-based quantum computing platforms will democratize access to quantum resources, enabling more researchers and companies to experiment with quantum algorithms without the need for costly hardware investments.
Ethical and Security Considerations
As quantum computing becomes more prevalent, ethical and security considerations will be paramount. Ensuring data privacy and developing secure quantum encryption methods are critical to building trust in quantum technologies.
Recommendations for Researchers and Developers
- Engage in Collaborative Research: Partner with academic institutions and industry leaders to stay at the forefront of quantum advancements.
- Prioritize Training and Education: Invest in training programs to equip teams with the skills needed to work with quantum technologies.
- Focus on Interdisciplinary Applications: Explore the intersection of quantum computing with other fields, such as AI and machine learning, for innovative solutions.
Conclusion
Google's collaboration with UK experts represents a significant step forward in exploring the practical applications of quantum computing. By harnessing the power of the Willow processor, researchers have the opportunity to solve complex problems across a variety of fields. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for quantum computing to transform industries and redefine computational capabilities is immense.
In my experience, the journey of integrating quantum computing into practical applications requires not only technical expertise but also a willingness to explore uncharted territories. The challenges are significant, but the rewards promise to redefine what is possible in computation.
FAQ
What is quantum computing?
Quantum computing is a type of computation that uses quantum bits (qubits) to process information. Unlike classical bits, qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously, allowing quantum computers to solve complex problems more efficiently than classical computers.
How does Google's Willow processor work?
The Willow processor operates using superconducting qubits, which are maintained at extremely low temperatures to reduce noise and increase stability. It utilizes advanced error correction techniques to improve performance and scalability.
What are the benefits of quantum computing?
Quantum computing offers the potential to solve complex problems in fields like chemistry, medicine, and cryptography, which are beyond the capabilities of classical computers. It can also optimize logistical and financial models for improved efficiency.
How can quantum computing enhance drug discovery?
Quantum computing can simulate molecular interactions at an atomic level, providing accurate models for drug interactions and potentially reducing the time and cost associated with drug discovery processes.
What are hybrid quantum-classical systems?
Hybrid systems combine quantum and classical computing to leverage the strengths of both approaches. This integration allows for more efficient processing of complex tasks that require both quantum and classical capabilities.
What challenges do researchers face with quantum computing?
Challenges include high error rates, scalability issues, and the need for specialized algorithms. Researchers must also address ethical and security considerations as quantum computing becomes more prevalent.
What is the future of quantum computing?
The future involves advancements in quantum hardware, the development of hybrid quantum-classical systems, and increased accessibility through cloud-based platforms. Ethical and security considerations will also be critical as technology evolves.
Key Takeaways
- Google partners with UK experts to explore quantum computing applications using the Willow processor.
- Quantum computing can revolutionize fields like chemistry and medicine by solving complex problems beyond classical limits.
- Implementation challenges include error rates, scalability, and the need for specialized algorithms.
- Future trends point towards hybrid systems combining classical and quantum computing for optimal performance.
- Cloud-based quantum computing platforms will democratize access to quantum resources.
- Ethical and security considerations will be paramount as quantum computing becomes more prevalent.
- Interdisciplinary applications of quantum computing can lead to innovative solutions.
- Training and education are crucial to equip teams with the skills needed to work with quantum technologies.
![[2025] Unlocking Quantum Potential: Google's Quest with UK Experts](https://runable.blog/blog/2025-unlocking-quantum-potential-google-s-quest-with-uk-expe/image-1-1765533339711.png)



